Special guest Ted Riederer shares the story of a New York artist who, as a gay street youth, made his mark with bold, conceptual graffiti. Blending street culture with high-concept art, his early works challenged boundaries, reshaped graffiti history, and paved the way for a pioneering career in immersive installations and social activism.
by Ted Riederer
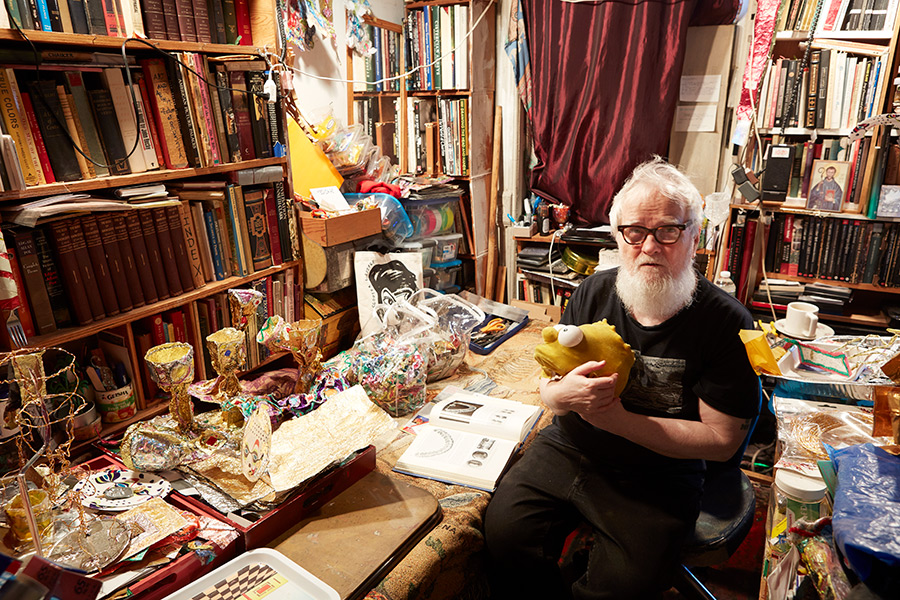
Thomas Lanigan-Schmidt, whose work is collected by prestigious institutions like the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the Whitney Museum of American Art, MoMA, and the Brooklyn Museum, and who was honored by President Barack Obama, began his career as a conceptual graffiti/street artist in the late 1960s. Known for his numinous sculptures and installations crafted from everyday materials like staples, cellophane, paper bags, and Scotch tape, Tommy’s journey started with a bold move. At just 20 years old, in 1968, he launched a spray paint stencil campaign on 4th Street in the East Village—a calculated street art action that reshaped and rewrites the many narratives of graffiti history.

I first met Tommy in 2004 at the School of Visual Arts, where he instantly became one of my favorite professors. In 2018, when I was the Artistic Director of Howl! Happening: An Arturo Vega Project, I co-curated an exhibition of Tommy’s work, which The New York Times described as a “revelation.” In preparation for the exhibit, Pavel Zoubok Gallery, along with the team at Howl, scanned hundreds of photographs and documents from the artist’s personal archive. We discovered a long-forgotten framed collage made from Village Voice clippings and photographs taped to a black plastic bag. This collage illuminates one of the first recorded acts of conceptual graffiti in New York City. An even more remarkable find was a handwritten manifesto from 1970, in which Tommy describes his philosophy behind this early work. This thoughtful and articulate document shows a level of sophistication beyond the artist’s years.
When I recently interviewed Tommy at the Mary Manning Wash Rehabilitation Hospital, he reflected on this formative period in his life. In 1967, after two semesters at Pratt, he ran away from his home in Linden, New Jersey. His father had derailed his artistic aspirations by enlisting Tommy as a ditch digger—ditch digging was the entry-level job for a career in construction. The night before his first day of construction work, Tommy fled home and hitchhiked to Times Square with 57 cents in his pocket.
Tommy found the Times Square scene to be “too rough,” so he made his way to the Village, where he found both safety and camaraderie among a vibrant community of gay street kids. One of these kids got him a job at an employment agency as a messenger. With regular, albeit meager, income, Tommy migrated east looking for cheap rent. He eventually found an apartment on 4th Street between Avenue B and C. He recounted, “I think the landlord rented to me because he didn’t think I would last very long. That neighborhood was really dangerous.”

Tommy, who often describes his life as full of unexpected, fortunate events, met the painter Christopher Scott on a corner outside the Museum of Modern Art after he couldn’t afford the entry fee. Scott was the partner of Henry Geldzahler, the curator of Contemporary Art at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. They adopted Tommy into their circle of friends and introduced him to the fecund theater scene that was thriving in the East Village. This scene included Charles Ludlam, Jack Smith, and John Vaccaro, along with institutions like La Mama Experimental Theater Club and Vaccaro’s Play-House of the Ridiculous. Tommy was deeply inspired by this new artistic community, especially Ludlam’s straightforward way of communicating, which avoided the pretentiousness often found in the Uptown art world.
Tommy described this period to me: “I was reading the Village Voice, reading John Perreault, and I said to myself, ‘I have to do something that connects with what they’re doing.’ So that’s how the street art happened. It was totally calculated, but it had to be true to who I am at the same time. Why graffiti? Graffiti was already considered art by the street kids, which was all the gay kids who I hung out with, but no one listened to them. I wanted to make something that wouldn’t look like graffiti but would be graffiti. It would have a conceptual element going through it, but it would have mostly a romantic element going through it. The reverie of being there was what I wanted it to be mostly about. This was art that couldn’t be bought. It had to be walked away from.”
Tommy instigated his project by sending a cryptic ransom note to Village Voice art critic John Perreault, signing it “Mr. T.” “I wanted them to think I was some crazy forty-year-old,” Tommy remembered. In a Village Voice article published on June 6, 1968, John Perreault wrote, “Recently I received a cryptic note in the mail. It was scrawled in ballpoint pen on green graph paper torn from a notebook, and it urged me to come and see ‘New York’s first real environmental art.’”

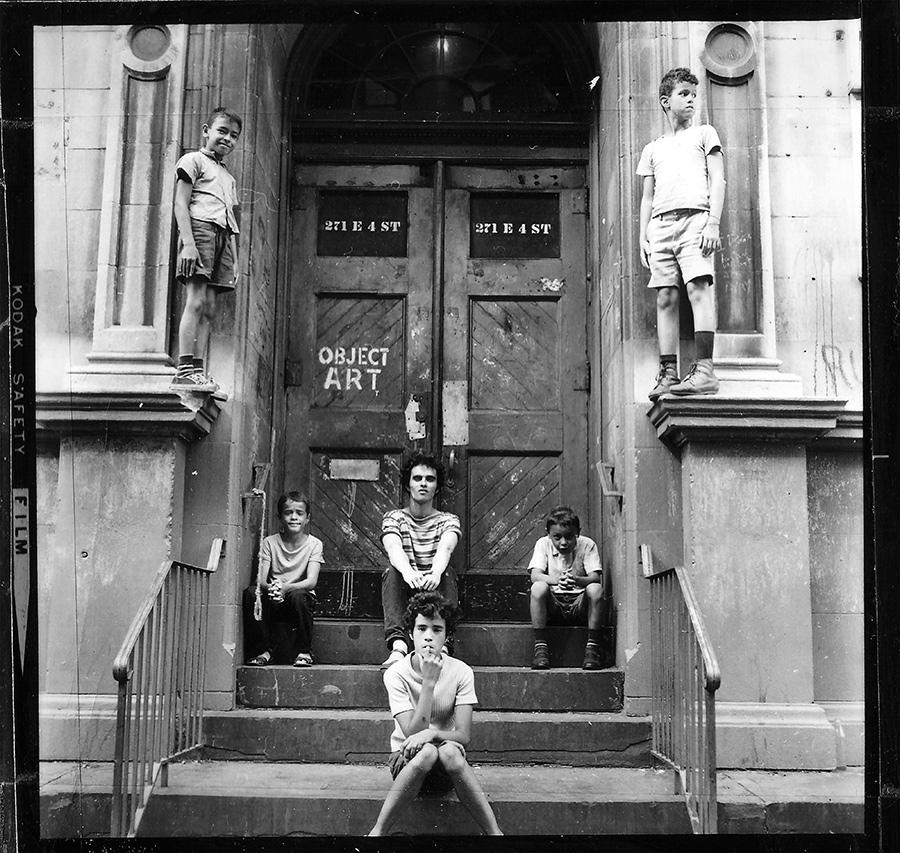
Tommy had covered 4th Street with a white spray-painted stencil that read “OBJECT ART.” In his 1970 manifesto, Tommy wrote, “Street graffiti was making the transition from the big sloppy paint brush to the more exacting use of the spray can. Conceptual art was isolating words as contemplative moments. The political atmosphere was sympathetic to the plight of the exploited and the underprivileged. I wanted to combine all these directions. I chose the name Mr. T to avoid identification. I chose the words ‘OBJECT ART’ from two definitions: Object as ‘a thing (an object)’; Object as the verb, to object (to object to something). And I wanted the words ‘OBJECT ART’ to hint at the expression ‘object d’art.’”

I spoke with Al Diaz, one of the graffiti artists behind the 2023 exhibition and book New York City of Kings: A History of New York Graffiti. I wanted to find out the state of graffiti in 1968 to fully understand the context of Tommy’s stencils.
Diaz explained, “Graffiti in the late 60s and 70s was more of a sport, quantity over quality. Julio 204 surfaces in 1967/68. It’s the first appearance of a name and number tag, even before Taki 183. What Tommy was doing was more ambitious. Instead of trying to communicate with the esoteric community of other taggers, Tommy was attempting to communicate with the public at large. Graffiti at the time was written by a local kid who addressed everyone in the neighborhood saying, ‘I’m here.’ It’s different than what Tommy was doing. He was appropriating that public space.”

Tommy wrote, “Partially following Leonardo’s advice to seek compositional inspiration in blots and stains on old walls, I isolated the most interesting walls, thought-provoking objects, and modified views through the placement of ‘conceptual graffiti,’ stenciled, as a viewfinder on or nearby the involving moments of vision. The experience of the ‘Art’ was constantly unformed and forming through confrontation with life, yet aesthetically informed through the view or moment of vision. It was done to confuse the participants into a state of creative tension between the ethical and the aesthetical.”
Scanned from the contact sheet cutouts in Tommy’s collage, photographer Robert Rosen’s beautiful photographs not only capture Tommy’s stencils, but they also document the transition from graffiti made with a brush to graffiti made with the spray can. One photo even captures the murmuration of carrier pigeons on the horizon. When I showed Tommy Rosen’s group portrait of kids from the neighborhood posing with an “object art” stencil, he exclaimed, “Those kids have to be in their 70s now.”
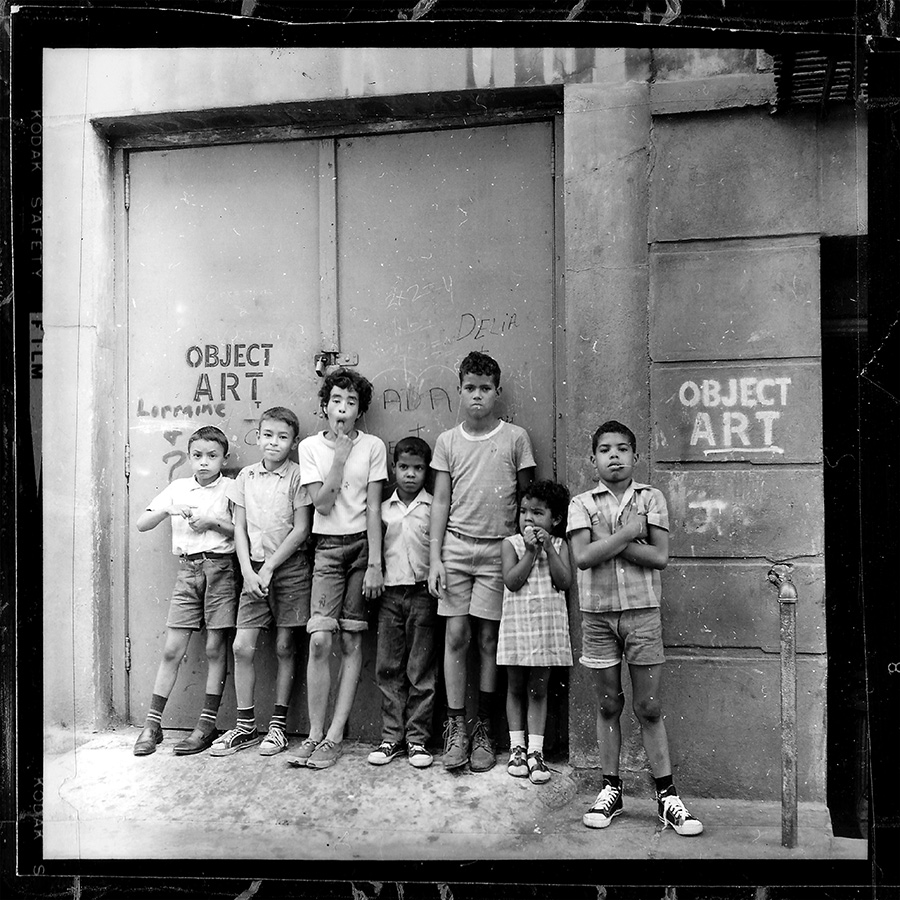

Tommy wrote, “Coming from a working-class background, I understood that the Bauhaus concept of people as bees in a hive was totally dehumanizing to the people it professed to help.”
This street art campaign was only the beginning. Tommy continued his practice with “environmental art,” transforming entire buildings into immersive installations and converting his own apartment into a gallery space. These endeavors were all featured in The Village Voice, with the gallery specifically highlighted in an article by Charles Ludlam.

The rediscovery of Perreault’s article from The Village Voice, Rosen’s photographs, and, most importantly, Tommy’s writings, is extraordinary. These documents provide insight into the early history of New York graffiti, a now ubiquitous global art form. This history also helps us understand the egalitarian underpinnings of an artist who is deeply concerned with social justice issues. Tommy was honored by President Obama in 2009 for his participation in the Stonewall rebellion and appears in front of the Stonewall with other youth in a well-known photograph by Fred W. McDarrah entitled Celebration After Riots Outside Stonewall Inn.

Al Diaz, who co-wrote SAMO with Jean-Michel Basquiat, reflects, “We didn’t understand completely what we were doing with our public writing project back then. Tommy’s art and writing help me define and understand more deeply what we were trying to do. Tommy’s stencils helped jumpstart his career just as SAMO helped jumpstart ours.”
Even though he has retired from teaching, Tommy continues to educate us through his work and the story of his life. He is actively making work from the bed of his rehab hospital. “Some of my best work,” he claims.

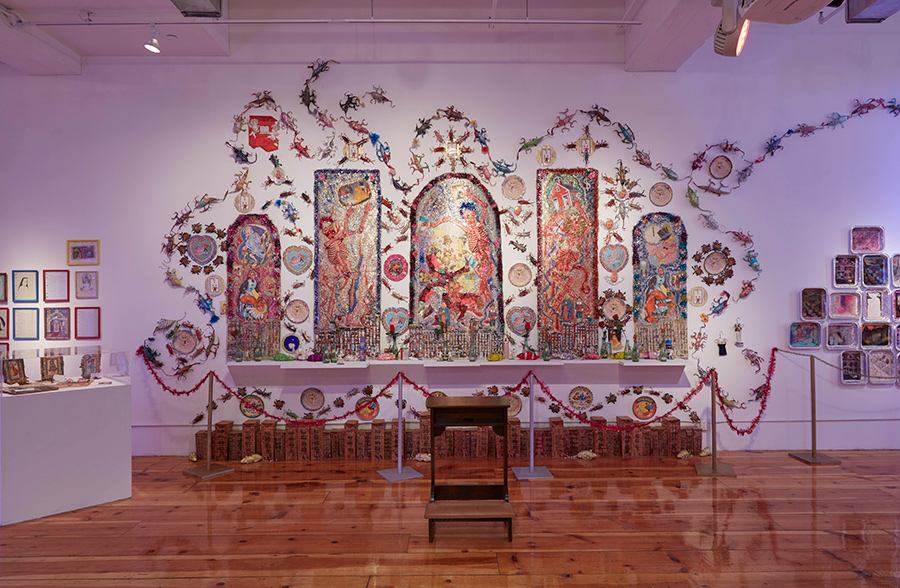
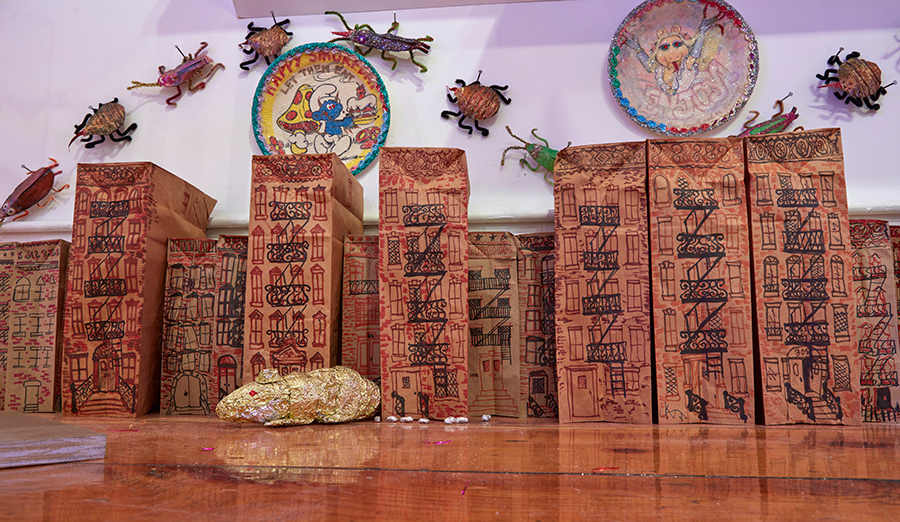
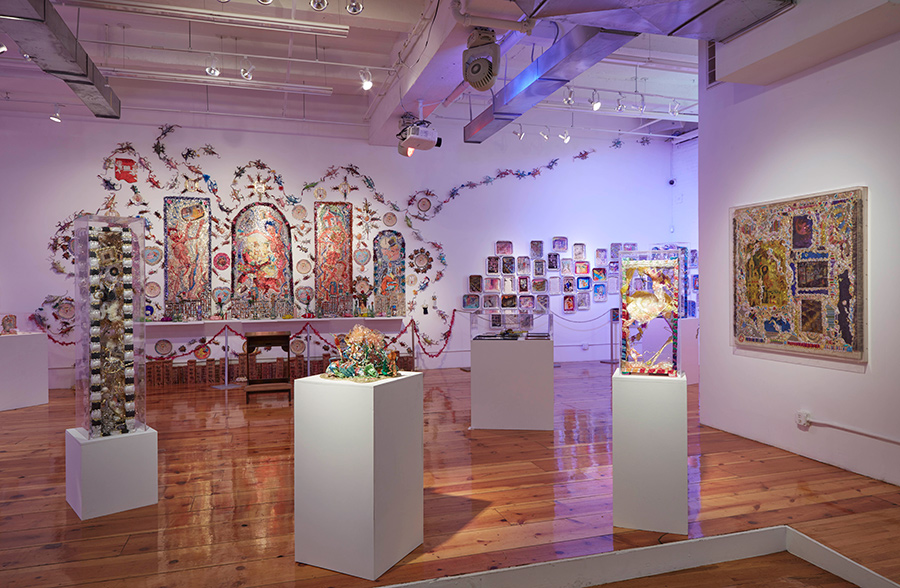
Scenes from Tommy Lanigan-Schmidt installation views from the exhibition Tenemental: With Sighs Too Deep For Words (Nov/December 2018).



About the Author: Ted Riederer
Described as a “one-time refugee from punk and sometime band member,” Ted Riederer has traveled the world equipped with painting supplies, electric guitars, amplifiers, old LPs, record players, drum kits, hard disk recorders, photography gear, a vinyl record lathe, and long-stemmed roses. His artistic journey has taken him from the Americas to the Antipodes, with his work exhibited both nationally and internationally at venues such as PS1, Prospect 1.5, Goff and Rosenthal Berlin, Nicole Klagsbrun Gallery, Jack Hanley Gallery (San Francisco), Marianne Boesky Gallery, Context Gallery (Derry, Ireland), David Winton Bell Gallery (Brown University), the University of South Florida Contemporary Art Museum, the Liverpool Biennial, and the Dhaka Arts Center in Bangladesh.
Riederer’s acclaimed project, Never Records, has traveled from New York to Liverpool, Derry, New Orleans, Texas, Kansas City, Brooklyn, Amman, and London, where it was sponsored by the Tate Modern. In addition to his artistic endeavors, Riederer served as the Founding Artistic Director of Howl! Happening: An Arturo Vega Project, a non-profit gallery and performance space in the East Village. The New York Times has recognized Howl! Happening as “instrumental to the history of the area.”
 BROOKLYN STREET ART LOVES YOU MORE EVERY DAY
BROOKLYN STREET ART LOVES YOU MORE EVERY DAY